
Silicone hydrogel (SiHy) contact lenses were introduced for the 1 day/daily disposable (DD) modality in 2008. Practitioners widely praised them for providing the additional physiological benefits of higher oxygen transmissibility (Dk/t) when compared to hydrogel (Hy) lenses.
However, early SiHy DD lenses fell short of Hy DD lenses in a key area: patient comfort.
That’s no longer the case.
SiHy 1 day lenses have evolved alongside the SiHy lens materials for other modalities. Since the introduction of early generation SiHy contact lenses, material technologies have advanced due to the use of lower modulus, resulting in less “stiffness,” or softer lenses.1
And the advancements in polymer science and material technology means that the latest generation of lenses no longer requires plasma oxidation, surface treatments, or even the addition of internal wetting agents.
Today, SiHy DD lens materials satisfy the needs of patients in the following key areas:
- Comfort
- Ocular health
- Ease of handling
- Availability for the most common types of vision correction
Retrospective analysis finds “no statistical differences” in comfort between silicone hydrogel and hydrogel daily disposable contact lenses
The Brien Holden Vision Institute funded five open-label trials to compare SiHy (delefilcon A, somofilcon A, narafilcon A) and Hy (omafilcon A, nelfilcon A) DD lenses. The findings were released in the January 2017 article “Comparison of Silicone Hydrogel and Hydrogel Daily Disposable Contact Lenses” (Diec et al).2
The Diec et al retrospective analysis of five studies includes multiple comfort factors. In their analysis they found no statistical differences—specifically:
“…no differences in comfortable wearing time were found between groups (P=0.41), and comfort at insertion, during day, and end of day was also no different (P≥0.71).”2 (See Figure 1)
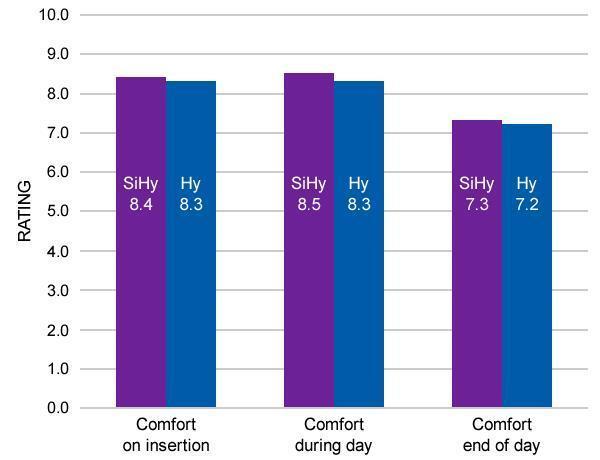
Each of the five trials required 40 participants “to be able to demonstrate a statistically significant difference of 1±1.4 points in comfort ratings on a 1 to 10 numeric rating scale with a 5% significance and 80% power.”2
Concerns about the comfort of early generation SiHy lenses were justifiable. As the Diec et al analysis shows, today’s SiHy lens materials put that concern to rest.
In addition, the latest generation of SiHy DD lenses are more affordable, making it easier for cost-conscious patients to switch from Hy to SiHy.
Ocular health advantages plus lens comfort make SiHy the material of choice for the DD modality
When deciding between two lens brands, patients now consider health one of the most important factors. Only vision quality ranks higher. (“The lowest price” ranks last in fifth place.)4
SiHy is the healthiest contact lens material* today. The question is: does its high Dk/t relative to Hy really make a difference in the DD modality?
As explained in “Why High Dk/t Matters in the Daily Disposable Modality,” the case for SiHy DD lenses can be summarized as follows:
- There’s no need to compromise. Despite the low risk of hypoxia-related signs and symptoms with current Hy DD lenses, the risks can be minimized if not eliminated with SiHy.
- Provides added protection for at-risk patients, including:
- Patients with greater oxygen demands.
- Patients whose vision correction needs result in thicker lenses, which can significantly impact oxygen transmissibility.5
- Longer wear time makes oxygen transmissibility even more important. The median daily wear time for 1 day contact lens patients is 14 hours.6
Conclusion
Today’s SiHy lenses are just as comfortable as hydrogel—the latest reason to prescribe SiHy for your 1 day lens wearers. In addition, the high Dk/t of SiHy DD lenses give them an ocular health advantage over hydrogel in their ability to minimize if not eliminate physiologic responses to hypoxic stimulus.
SiHy DD lenses also satisfy patient needs for ease of handling and are available to treat the most common types of vision correction. Finally, current SiHy lenses are also more affordable than their predecessors.
That adds up to five reasons to make SiHy your material of choice for the DD modality.
See also:
- Infographic: Why is silicone hydrogel (SiHy) the right choice for 1 day contact lenses. Summarizes key evidence for choosing SiHy daily disposable contact lenses over hydrogel for your patients.
- What are contact lens wearers willing to pay? 95% of wearers who say ocular health is important are willing to pay more for contact lenses that ensure eye health.
Sources:
1. Tighe BJ. A Decade of Silicone Hydrogel Development: Surface Properties, Mechanical Properties, and Ocular Compatibility. Eye Contact Lens. 2013;39(1):4-12.
2. Diec J, Tilia D, Thomas V. Comparison of silicone hydrogel and hydrogel daily disposable contact lenses. Eye Contact Lens. 2017. DOI: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000000363 [Epub ahead of print].
3. Ibid. Chart is a re-creation of the chart in the Diec et al article.
4. Hanover Research study. What are contact lens wearers willing to pay? InSight Newsletter. July/August 2016.
5. Lira M, Pereira C, Real Oliverira ME, Castanheira EM. Importance of contact lens power and thickness in oxygen transmissibility. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2015;38(2):120-126.
6. Dumbleton KA, Richter D, Woods CA, et al. A multi-country assessment of compliance with daily disposable contact lens wear. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2013;36(6):304-312.
*Data on file. With higher oxygen permeability than hydrogel materials, silicone hydrogel contact lenses minimize or eliminate hypoxia-related signs and symptoms during lens wear.





